Shin Splints (Tibial Stress Syndrome)
Footlogic: The science of walking comfort
Articles in this section
Symptoms:
The term shin splints denotes pain or inflammation in the anterior or medial section of the tibia. The patient presents with tenderness and pain along the border of the tibia, especially after sports activities, running or long walks. Usually the pain will settle upon resting.
Causes:
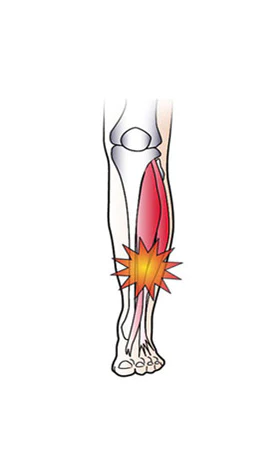
A third condition is lateral shin splints which occurs as a result of excess supination or a high forefoot valgus deformity.
Treatment:
Common treatment modalities include ice therapy, rest, deep tissue massage and exercises to stretch and strengthen the tibial muscles. Orthotics can also be effective for patients presenting with excess pronation. By correcting excessive pronation Footlogics orthotics reduce internal tibial rotation and medial tractional forces upon the anterior tibialis and posterior tibialis muscles.
In the case of lateral shin splints the patient may exhibit a forefoot valgus deformity, which will require a forefoot valgus wedge to be added to the orthotic.

