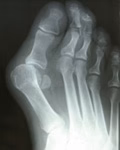
Hallux Abducto Valgus (Bunions)
Footlogic: The science of walking comfort
Articles in this section
Symptoms:
A bunion is a valgus deviation of the hallux commonly associated with an exostosis on the 1st metatarso-phalangeal joint. When irritated by tight or ill-fitting shoes bunions can become red and swollen.
Causes:
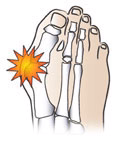
A short 1st metatarsal and Excessive pronation
A short 1st metatarsal will adduct and drop to meet the ground during the toe-off phase of gait. Excessive pronation causes excessive forces to be applied to the medical forefoot area, with increased load on the 1st metatarsal head in an adductory direction, hence the term ‘Hallux Abducto Valgus’.
Some bunions are caused by arthritis or trauma. Due to excessive pronation, forces load the medial forefoot area. This increased adductory load on the 1st metatarsal shaft causes rotation of the shaft, which then requires the hallux (big toe) to compensate by abducting.
Treatment: